Last Updated JULY 2023
Why are modern manufacturers focusing on Agile R&D?
In this article, we’ll cover how Agile drives manufacturing R&D, and how R&D is a launchpad for manufacturers to spread Agile across their organisations.

Agile methodologies can be applied more naturally to R&D than any other manufacturing function. As such, R&D is often the first place — outside of software development — where manufacturers implement Agile in order to respond better to changes in customer and market demands.
From pioneering R&D projects, manufacturers can scale Agile up across technologies and into new functions, such as production, maintenance and supply chain management.
Product development: why Agile and not linear?
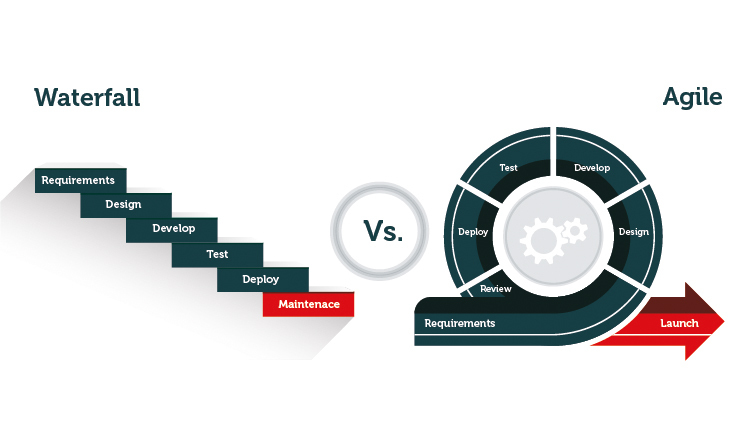
The traditional approach to product development has often been linear — popular examples are the Waterfall and Stage Gate models. These development models manage project progression linearly where tasks are completed in sequential steps.
These models use a predictive approach to conceptualise, plan, execute and control work to achieve project objectives within a specific timeframe. Because these approaches define the project deliverables and timelines from the outset, they are suited to simpler, smaller and lower-risk projects that have clear and unchanging requirements.
Linear-sequential development models are more challenging to implement for complex product development projects as it is difficult to foresee and address every risk before the project kicks off. And as the model phases do not overlap, it can be difficult to revisit and revise previous development stages after receiving customer feedback or test results.
Many of the limitations of linear product development models are addressed by using agile principles in R&D. At its core, Agile product development involves building products in short iterations, promoting continuous feedback and rapid improvement.
Its focus on smaller outcomes makes it less rigid compared to traditional product development approaches as it allows close-knit teams to evaluate objectives, progress and obtain results rapidly and continuously. Manufacturers can respond quickly and fluidly to change without being confined to rigid stage gates — small parts of the product can be built and tested simultaneously, which ultimately leads to a more efficient allocation of resources and drastically improved speed-to-market.
Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management
4 Considerations to make your R&D more Agile
1. Task Management
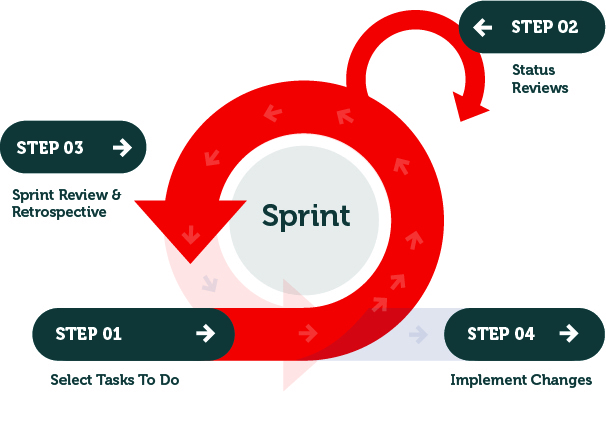
The Agile methodology in R&D involves breaking down long product development processes into smaller, more manageable projects. These mini-projects are managed using established approaches such as the “Scrum” process.
One critical element of Scrum is time-boxed iterations, known as Sprints. Each Sprint will progress iterations of a product through the entire product development process with the potential for launching a new product or feature at the end of a Sprint.
The Agile Sprint Process Simplified
Each Sprint focuses on completing specific critical tasks, reviewing progress and implementing changes. For R&D, this can involve implementing incremental changes, creating prototypes and testing to identify and address problems early on before they become major issues.
2. Early Prototyping
Early prototyping is a way for manufacturers to learn more, faster. By creating smaller and more frequent updates in the form of digital or physical prototypes, manufacturers enable quicker feedback loops to learn from failure, validate assumptions and react faster to market changes.
3. Team Collaboration
“A collaborative governance structure that engages the cross-functional team throughout the decision-making process is critical. A governance structure that serves as a rubber stamp after the real decisions are made elsewhere is not helpful in improving agility,” said Stuart Poulton, former Vice President for Portfolio Program Management at AbbVie.
Self-organised teams that have clearly defined roles and responsibilities within the group are focused on driving solutions towards delivery. The right tools and techniques, such as daily stand-ups, collaboration tools and integration software help to increase team autonomy, eliminate departmental silos and improve team synchronisation.
4. Customer Integration
Involving the customer in the product development process ensures that customer feedback is always considered. Checking market fit and benchmarking against customer expectations can improve customer integration, enhance product quality and lead to faster and more consumer-centric product iterations.
Driving Agile R&D with Kimberly-Clark ProfessionalTM cleaning
Here at Kimberly-Clark ProfessionalTM, we understand that the most effective solutions are developed from rapid iteration and regular testing across multi-functional teams. In fact, we use the same Agile Sprint process to develop our specialist range of cleaning products and solutions.
We can integrate with our customers’ R&D team through our sprint process to fast-track product development and facilitate scale-up to production. In addition to our comprehensive product and solution range, our client partners can benefit from our experience and expertise to realise the right cleaning solutions in parallel with product development. We believe that our willingness and ability to get involved with customer R&D, supply test materials, and provide in-depth product data make us the best R&D partner for agile product development.
Your digitalised future
We would love to partner with you to start implementing the best agile cleaning solutions for your organisation. Interested? Take the next step now:
Biography:

Patrick Roche
Senior Product Developer with a total of a decade of experience within the Kimberly-Clark Professional™ R&D Team, focussing on Wiping Solutions.