Last Updated APRIL 2024
The Strategic Significance of Traceability in Recycling

In this post, we'll cover:
- » Understanding Traceability in Recycling
- » 5 Benefits of Traceable Recycling
- » How to Better Track Your Waste Streams
- » Overcoming Key Implementation Challenges
Embracing traceability means taking ownership of your waste management practices transparently — and with documentation.
The call for environmental stewardship isn’t just a “side note” in corporate strategy, but a huge driving force in shaping brand reputation. Sustainability and recycling have moved far beyond eco-fads to become core principles of corporate responsibility.
It’s becoming increasingly clear: what's good for the planet is also necessary for businesses to thrive.
Traceability emerges as a critical yet often overlooked component of sustainability, providing a clearer pathway toward achieving your corporate sustainability goals — while underscoring your commitment to environmental responsibility. In this article, we’ll delve into why traceability in recycling isn’t just an optional addition to your sustainability efforts, but a strategic imperative ensuring complete alignment with a sustainability-driven marketplace.
Understanding Traceability in Recycling
What is traceability in the context of recycling, and why should it matter? Traceability is the meticulous tracking of waste from the beginning of the recycling process to its final disposition.
This diligent method of tracking addresses a significant sustainability blind spot – once waste leaves your facility, it’s not 'out of sight, out of mind'. Instead, its journey post-discard directly impacts your organization's environmental footprint.
Embracing traceability means taking ownership of your waste management practices transparently — and with documentation.
Traceability aims to create a closed-loop system, reintegrating recycled materials into the manufacturing cycle. This objective is more than idealistic; it's a practical business strategy that minimizes waste, boosts operational efficiency, fosters resource renewal, and may even uncover new revenue opportunities.
Maximize Your Efficiency — 5 Benefits of Traceable Recycling
Beyond the ethical advantages, there are clear and measurable returns to investing in this approach. Let's examine the benefits of incorporating traceability measures into recycling systems.
Environmental Footprint Reduction
Detailed tracking provides organizations with a comprehensive understanding of their resource consumption and waste generation, revealing inefficiencies in waste management processes. With this insight, organizations can proactively develop strategies to minimize waste, optimize resource use and reduce energy consumption.
Transparency and Accountability
By harnessing robust data, businesses can effectively showcase their sustainability efforts to stakeholders and regulatory bodies with concrete evidence. Embracing traceability ensures strict adherence to accountability standards, enabling accurate reporting on waste management practices. This heightened transparency strengthens stakeholder relationships and positions organizations as leaders in sustainability.
Compliance with Regulations
Meticulous documentation at each stage of the recycling process ensures strict compliance with environmental regulations. This transparency enables businesses to document waste management practices, rectify any non-compliance promptly and avoid penalties. Embracing traceability not only meets legal requirements but also demonstrates dedication to environmental responsibility.
Improved Resource Management
Traceability enhances resource management by offering insights into recyclable material life cycles, fostering innovation. Real-time tracking improves inventory management, enabling informed decisions that optimize resource use, cut costs and promote sustainability throughout the recycling chain.
Creating Potential Revenue Streams
Every byproduct of consumption holds the potential for a second life. Traceability in recycling facilitates the 'trash-to-cash' concept, turning waste into valuable resources. Through strategic partnerships, organizations can sell recyclable waste to be repurposed, creating potential revenue streams. This approach not only contributes to environmental sustainability, but also demonstrates an innovative mindset in operational efficiency.
From Bin to Data — How to Better Track Your Waste Streams
Now that we’ve established the importance of traceability, the question becomes: how do we do it?
Let’s explore a few strategies to help organizations tackle the challenge of implementing effective traceability in their waste management processes.
Start by Conducting Waste Walks
Consider starting with regularly
scheduled waste walks — the unsung heroes of waste
management. These audits yield critical data that unveils the true volume, composition and fate of your waste. Armed
with this information, you can identify recycling opportunities and areas for operational overhaul to minimize
unsustainable waste pathways. Waste walks can also be a great way to get collective buy-in toward your
sustainability initiatives as it requires stakeholders to walk the process together and take ownership over specific
tasks.
Explore Advanced Technologies for Enhanced Waste
Monitoring
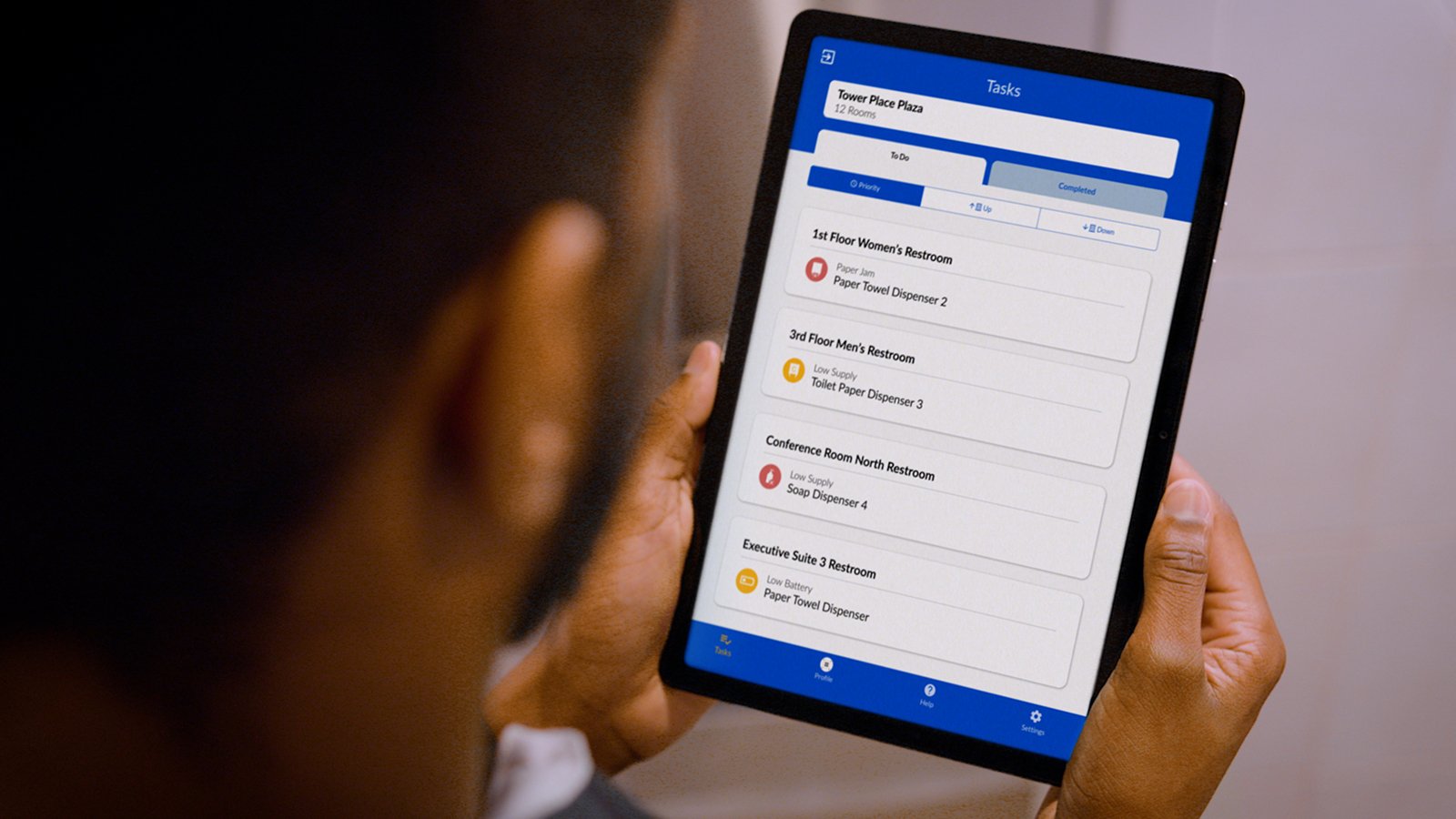
Digital innovations have transformed waste management, enabling organizations to monitor recyclable materials with
unprecedented precision throughout the entire process.
By implementing digital solutions, organizations gain visibility into waste movement, optimize collection routes and ensure better compliance using the following tools:
- Barcodes and Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) Tags — Attached to bins or items enabling precise identification and seamless tracking for streamlined data and enhanced inventory management.
- GPS and Geotagging — Used to track the location and movement of recycling vehicles, bins and materials for efficient route planning, asset management and monitoring of collection and transportation activities.
- Blockchain Technology — Provides a decentralized and immutable ledger system that tracks the life cycle of recyclable materials, ensuring transparency, traceability and accountability.
- Sensor Technology — Embedded into recycling bins, containers or sorting equipment, sensors enhance data collection on fill levels, material composition and processing parameters for process optimization and compliance monitoring.
- Data Analytic Platforms and AI — These platforms can analyze large volumes of recycling data to identify patterns, trends and areas for improvement, providing valuable insights into process optimization.
Through The RightCycle™ Program, Kimberly-Clark Professional partners with Wastebits, a software solution designed to help organizations streamline their recycling operations and provide improved traceability. By collecting real-time data on material composition, fill levels and processing parameters, Wastebits optimizes recycling processes, ensures compliance with regulations and reduces waste.
Build Partnerships and Leverage Their Expertise
Forming collaborative partnerships with waste management experts is essential because it provides invaluable access
to specialized industry knowledge and experience. This expertise enables organizations to develop more effective
waste-tracking strategies and implement tailored best practices.
These partnerships also offer access to new technologies that enhance traceability efforts, enabling organizations to achieve their sustainability goals more effectively.
Overcoming Key Implementation Challenges
Adopting traceability in recycling is not without its hurdles. Common challenges include upfront costs, integrating new technologies into existing systems and the human factor — employee and stakeholder resistance to change.
Raising Awareness and Cultivating Stakeholder Buy-In:
Shifting toward traceability is more than just an operational improvement; it's a cultural transformation. Some
team members may not understand the importance of traceability and its connection to their roles and the
organization's sustainability objectives. This can lead to the perception of traceability as a burden —
disrupting workflow and raising concerns about increased workload.
Solution:
- Establish open communication channels to address concerns or misconceptions about increased workload or shifts in responsibilities.
- Provide comprehensive training emphasizing how traceability enhances efficiency, regulatory compliance and environmental responsibility, aligning with organizational goals.
- Ensure that leadership visibly supports traceability, championing its importance to encourage widespread adoption.
Navigating Technological Transitions:
Incorporating new technologies into current systems can cause compatibility issues and temporary disruptions,
revealing inefficiencies. Employee training may face resistance due to concerns about job displacement or skepticism
about the benefits. Also, to gain support from leadership and stakeholders, a clear justification for the upfront
costs may be required.
Solution:
- Involve stakeholders in developing and implementing the transition plan, fostering a sense of ownership.
- Provide evidence of the ROI, including cost savings, efficiency improvements and environmental benefits to gain support.
- Pilot new technologies on a smaller scale before full-scale implementation to identify and resolve issues early.
- Implement comprehensive training programs to educate and build familiarity with new technologies.
Overcoming the Cost Barrier:
As with any sustainability endeavor, cost is a significant concern. Upfront investments in software, equipment
and training pose barriers, especially for organizations with limited budgets. Despite long-term benefits like
improved efficiency and reduced waste, organizations may struggle to justify the initial costs in the short
term. Disruptions during implementation can also temporarily decrease operational efficiency, adding to concerns
about overall cost-effectiveness.
Solution:
- Explore if there are any government incentives or grants available in your region or industry to help offset the upfront costs.
- Collaborate with industry partners, suppliers or waste management companies to share the costs, resources and expertise.
- Identify opportunities to streamline internal processes and optimize resource utilization to help minimize costs.
A Call to Action for Traceability
The journey towards sustainability is an ongoing process, marked by innovation, resilience and unwavering commitment. Traceability in recycling serves as a crucial touchstone, providing a tangible measure of progress and a guide to the path ahead. By tracing the life cycle of materials, we can identify opportunities for improvement, optimize resource utilization and ensure that our efforts toward sustainability are effective and impactful. With each step forward, we move closer to a more sustainable and resilient world.